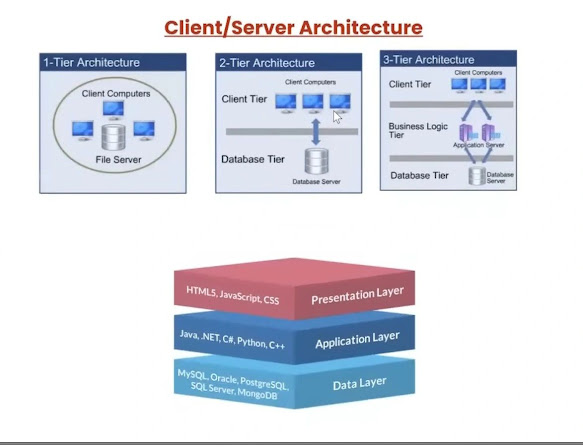
- 1-Tier - It has only 1 client and 1 server.
- 2-Tier - It has multiple clients but contains only one server.
- 3-Tier - It will have 3 layers.
- Application - It works for a Web Application. It is called an Application Layer.
- Programming - we will send API requests through code which are written in programming languages(Eg: java, python etc.).
- Interface - It will act as an interface or communication barrier between client and server.
- Generally, we test the UI using selenium and we check whether every functionality is working or not. But, when it comes to API Testing we send a request to the server based on the request it will give the response. In the response itself, we can check whether all the functionality is working or not. 80% of the Testing is completed within less time if you know API Testing and 20% will be testing the UI elements, colour buttons etc.
- No need for UI Testing by 100%.If we perform API Testing.
- We can perform API Testing once the backend code and the APIs are ready. A gap will occur between the presentation and Application layer(it will take time to create UI). In that time, we can test our application using API's.
- API Testing is simple and easy to learn compared to Selenium web application Testing.
👋 Hi, I'm Suriya — QA Engineer with 4+ years of experience in manual, API & automation testing.
📬 Contact Me | LinkedIn | GitHub
📌 Follow for: Real-Time Test Cases, Bug Reports, Selenium Frameworks.